Efficacy of treatmentback painit directly depends on how accurately it is delivereddiagnosis. . . However, the pain syndrome itself is not a characteristic symptom - it is a general symptom, according to which it is impossible to determine the cause of the disease. There are many different pathologies that can cause itback pain, and not all are associated with diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
When self-medicating, patients mistakenly believe that the most important thing is to deal with the pain, and they lose sight of the fact that every pain has a cause. Taking pain medication is a symptomatic treatment that affects neither the outcome of the disease nor the cause of the pain.
The main causes of back pain
Consider the main onesdiseaseprovocationback pain. . . To make the diagnosis easier, doctors divide the back into the upper (cervical spine), middle (thoracic spine) and lower (lumbosacral) parts.
Pain in the upper back
Pain in the cervical spine requires the utmost attention. The reason is in the unique anatomical characteristics of the cervical vertebrae: the vertebral artery passes through them, supplying blood to the brain; the first and second cervical vertebrae form a mobile complex articulation with the skull, which is responsible for turning and tilting the head; any disease that occurs at this level has the potential to cause serious neurological damage, as damage or even small compression of the spinal cord in the cervical spine immediately leads to impaired motor and / or sensory function in the rest of the body.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine
Normally, the intervertebral discs, joints, ligaments and tendons do not have their own blood vessels, their blood supply depends on how intensively the nearby muscles and bones are supplied with blood. If this process is disturbed, for example, in an office worker who leads a sedentary and sedentary lifestyle, degenerative-dystrophic changes begin in them. The nutrition of the cartilage of the intervertebral discs and joints is disturbed, ligaments and tendons thicken, due to sclerotic changes, the spinal canal narrows and the distance between the vertebrae decreases.
Among non-specialists, this disease is known as osteochondrosis of the spine. Despite the fact that degenerative-dystrophic processes are characteristic of the entire spine, osteochondrosis is the most common cause of pain in the cervical spine. Moreover, as in other parts of the spine, this disease can be complicated by an intervertebral hernia. However, due to the peculiarities of the anatomy of the cervical spine, even a small hernia can cause serious complications.
Trauma
Although spinal cord injury is more commonly diagnosed in the lumbar spine, almost 50% of cases of spinal cord injury occur with trauma to the cervical spine. This is due to the peculiarities of the anatomy of the neck: the absence of a developed muscular frame and massive vertebral bodies, high mobility contribute to trauma even without direct physical impact (for example, with a sudden stop or blow from the back during accidents, often occurs so-calledbending followed by sharp extension of the cervical spine). Pain is a constant companion of every spinal injury.
Myositis
Myositis or inflammatory muscle disease is a whole group of diseases characterized by muscle pain. The most common cause of banal muscle inflammation is forced posture when performing any work, hypothermia, draft. Muscle pain can be caused by osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, intervertebral hernia - the muscles take over most of the load on the neck, which ultimately leads to overexertion, muscle cramps with impaired microcirculation and inflammation.
Neuralgia
Neuralgia is a condition in which nerve fibers themselves become a source of constant impulses of pain. The pain is paroxysmal, it can be intensified and caused by turning or tilting the head, in cold weather. The cause of neuralgia is associated with diseases of the spine - osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernia, scoliosis, etc. The immediate cause of pain is irritation of the spinal cord roots when they are compressed in the intervertebral space, muscle spasm, which disrupts the metabolism in the nerves that pass through the spasmodic muscles. Unlike neuritis or inflammation of the nerve, in neuralgia the pain is periodic, there are no pathological changes in the nerve fibers themselves.
Heart disease
Heart diseases such as angina pectoris, ischemic heart disease, coronary atherosclerosis are often accompanied by pain radiating to the neck, lower jaw, shoulder and left forearm. The pain may be accompanied by numbness, tingling in the skin, simulating pain in osteochondrosis of the cervical spine with an intervertebral hernia. Often patients receive massage, physiotherapy, visit other doctors, although an electrocardiogram is sufficient to diagnose the cause.
A characteristic feature of such pain is the ability of antianginal drugs that improve blood flow through the coronary arteries (isoket, nitroglycerin) to relieve pain within minutes.
Pain in the middle of the back
The thoracic spine consists of 12 thoracic vertebrae, each of which has a pair of ribs attached. Together they provide protection for the thoracic organs. The size of the thoracic vertebrae gradually increases, starting from 1 thoracic vertebra and further to the beginning of the lumbar spine - this is explained by the gradual increase in the load on them. The mobility of the middle part of the back is significantly less than the mobility of the neck, the ribs provide additional protection, due to which traumatic spinal cord injuries in the thoracic part of the spine are less frequent.
Curvature of the spine or scoliosis
Scoliosis or scoliotic disease is a pathological curvature of the spine in several planes. The causes of scoliosis are still not exactly known, the disease begins in childhood. Lack of physical activity, weakness of the back muscles, improper posture and organization of the workplace of schoolchildren are considered factors that contribute to this. Due to the pronounced curvature, disturbed load distribution and biomechanics of the spine, muscle strain that compensates for part of the load,to arisechronicback pain.
Arthritis (spondyloarthritis)
The intervertebral joints together with the intervertebral discs connect the spine into one whole. Each vertebra has 4 articular surfaces that form joints with adjacent vertebrae. Like any other joint, the intervertebral joints can become inflamed. This pathological condition is called spondyloarthritis. There are two main causes of inflammation of the intervertebral joints. These are systemic rheumatic diseases (such as rheumatoid arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis) or reactive inflammation that occurs in response to increased stress in osteochondrosis, scoliosis and other pathologies of the spine. Inflamed joints lose function: stiffness of movement, stiffness of the spine, prolonged back pain.
Gastrointestinal disorders and back pain
Abdominal diseases are often the cause of reflected pain in the back and spine. There is also a direct connection between pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Diseases such as chronic colitis or gastroenteritis are the background for spondyloarthritis or osteochondrosis of the spine.
Most often, back pain is reflected in ulcers of the stomach and duodenum, hiatal hernia, acute or chronic pancreatitis. This phenomenon arises from the specificity of the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems, whose nerve fibers are present in every organ of the abdominal cavity. Part of the pain impulse they perceive returns to the roots of the spinal cord, simulating pain in the spine and back.
Kidney disease and back pain
The kidneys are a paired organ located in the retroperitoneal space, which, as in the case of the abdominal organs, is intimately connected to the nerves with the roots of the spinal cord. In the presence of inflammation, stones or other pathologies of the urinary tract, part of the pain impulse reaches the spinal cord, simulating a disease of the spine.Symptoms of back painmay occur in acute pyelonephritis, renal colic, renal abscess. A characteristic symptom is tension in the back muscles in the projection of the kidneys, which occurs due to inflammation of the kidneys or abscesses in the tissues that surround them.
Pain in the lumbosacral spine

The lumbosacral spine has the greatest stress. Up to 60-70% of the adult population of developed countries complain of back pain. This is a favorite localization of intervertebral hernias. One patient is most often diagnosed with 2-3 hernias in the lumbosacral spine. Also, pain in the lower back and sacrum often occurs in gynecological and urological pathologies.
Intervertebral hernia
Intervertebral hernia is the result of long-term osteochondrosis of the spine. While relatively small loads are applied to the intervertebral discs in the cervical region, in the lumbosacral region each disc has enormous pressure. A healthy disc can compensate for any weight, thanks to the semi-liquid core, which acts as a hydraulic shock absorber. However, due to osteochondrosis, the fibrous and strong cartilage (annulus fibrosus) that goes along the periphery of the intervertebral disc loses elasticity and strength, and some parts of it can crack. With a sudden increase in load, for example, when lifting weights, the pressure inside the diseased disc increases, which is why its contents can actually "shoot" through the damaged cartilage, falling into the lumen of the spinal canal - thus forming an intervertebral hernia.
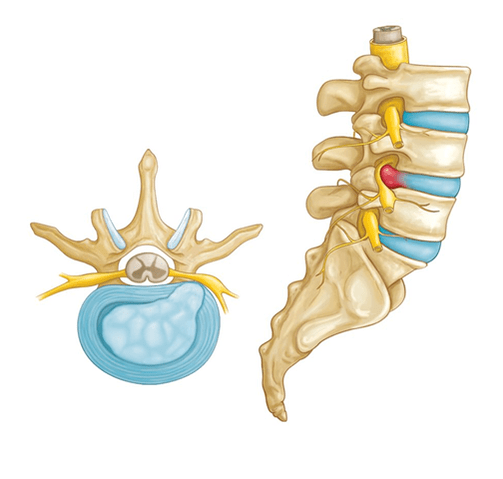
Fragments of the nucleus that fell out of the disc compress the spinal cord and spinal root. As a result, the nervous tissue swells and blood circulation is disturbed, which is accompanied by severe pain and protective muscle spasms. The pain can be unbearable, all the way to the need to use narcotic analgesics. A characteristic feature is the radiation of pain in the lower extremities. Disorders of sensitivity to pain, tingling and numbness of the skin of the lower leg and thigh may occur.
Intervertebral disc protrusion
The main difference between intervertebral disc protrusion and hernia is the preservation of the integrity of the fibrous annulus. The cause of pain is compression of the spinal cord and its roots by protrusion along the periphery of the intervertebral disc. However, if the process continues, the bulge can easily turn into a hernia. The symptoms and pain are similar to those of a herniated disc, because the severity of the pain syndrome depends not only on the size but also on the location of the bulge or hernia.
Spinal spondylosis
Excessive loads and degenerative-dystrophic processes in the spine can lead to ossification of cartilage tissue, which is saturated with calcium salts and turns into sharp growths of coracoid bone or growths that occur along the periphery of the vertebral body. As the process progresses, these growths may merge with the same growths on the body of adjacent vertebrae. Over time, all the vertebrae grow with each other, the spine loses its flexibility and elasticity. Pain occurs due to irritation of the spinal cord and its roots, reactive inflammation and dystrophy of soft tissues, ligaments and muscles that surround the spine.
Radiculitis
Radiculitis is an intense pain caused by circulatory disorders and ischemia of the spinal cord roots, strangled by a hernia or bulge with osteochondrosis of the spine. Various disorders of skin sensitivity in the buttocks, perineum, thighs and lower legs are possible. Initiated sciatica leads to muscle atrophy and weakness. A characteristic symptom is shooting pains along the sciatic nerve, which worsen when moving, lifting weights and in cold weather. This condition is called sciatica or sciatica.
Spine infection
The vertebrae are made up of spongy bone tissue rich in bone marrow. When the infection enters the bloodstream in the vertebral body, an inflammatory process can occur - osteomyelitis. Gradual deterioration of bone tissue is accompanied by necrosis - this picture is also typical for spinal tuberculosis. Pain can occur both due to irritation of nerve endings and due to pathological compression fractures of the spine, weakened by inflammation.
Gynecological and urological diseases
Pathologies such as cervical cancer, endometriosis or adnexitis (inflammation of the uterine appendages) in women, prostatitis or prostate cancer in men are often accompanied by severe pain in the lumbosacral spine. The nature of the pain is explained by irritation of the nerves affected in the area of inflammation, or the growth of nerve trees by the tumor.
The back muscles ache along the spine
Well-developed back muscles are a sign of a healthy spine, because a muscular corset relieves some stress and additionally stabilizes the spine. In chronic diseases of the spine, the muscles are subject to excessive loads that weak and atrophied muscles cannot withstand. As a result, muscle spasms occur, and due to metabolic disorders in the muscles and pain. This condition is called myofascial syndrome, which is characteristic of osteochondrosis of the spine, hernia and protrusions of the intervertebral discs.
Postoperative pain
Spinal surgeries are usually accompanied by extensive trauma - to stabilize and restore the integrity of the spine, doctors may resort to implanting metal structures, screwing screws into vertebrae, and removing unsustainable tissue. The pain in this case occurs not only because of the disease itself, but also because of the operation. With proper rehabilitation and postoperative care, the pain will gradually disappear. However, if you ignore your doctor’s instructions and neglect mandatory exercise in the postoperative period, the pain can become chronic.
How are the causes of back pain diagnosed?
To diagnose back and spine pain, it is necessary to seek medical help in time from a qualified neurologist. In the first phase, a neurological examination, examination of the patient, study of reflexes and symptoms are performed. An experienced and competent doctor knows well which diseases of back and spine pain he has for certain reasons and characteristic features.
Back pain for no apparent reason should be especially careful. This can be with reflected pain of other organs and systems, with tumors and diseases of the spinal cord.
To find out why your back and spine hurt, a neurologist may prescribe magnetic resonance imaging. It is the most effective and safest method for diagnosing almost all possible causes of back pain. The procedure is based on the ability of magnetic fields and radio waves to give clear and detailed images of the spine and spinal cord without the use of X-rays and other harmful factors.
How to relieve back pain
To alleviate, but not treat back pain, we take analgesics for a few days, which is necessary to wait for a consultation with a specialist. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs or NSAIDs are most commonly used for this purpose. However, it is important to keep in mind that this group of drugs can cause dangerous side effects, the likelihood of which increases with prolonged use. That is why it is important that you do not postpone the visit to the doctor and the examination.treatmentdiseasesspineand reasonsback pain.
Treatment of back pain
As stated at the outset, the effectiveness of treating back pain depends on how accurate the diagnosis is. Despite the obvious, many patients "cure" pain for years, but not the disease itself, each time postponing a visit to the doctor, turning to traditional healers, osteopaths and chiropractors. Moreover, for some spinal diseases, such procedures are not only contraindicated but dangerous.
There are effective and scientifically proven treatments for variousspeciesdiseases they causeback pain. . . Many of them require the patient’s perseverance and persistence in fighting the disease. It is important to remember that there are no pills or injections that can cure osteochondrosis - only you can do that, with hard training and physical exercises that a neurologist will show you.
Which doctor should I go to for back pain?
Back pain is one of the most common neurological symptoms that occur due to the involvement of nerves and spinal cord in the pathological process. Therefore, the first specialist, whose consultation should be obtained in case of back pain, will be a neurologist. Based on the results of the examination and magnetic resonance imaging, you may need to see another doctor. If the back pain is caused by heart disease, the patient is referred to a cardiologist, if the problem is in the digestive tract, a gastroenterologist. But most often the pain syndrome is associated with the pathology of the spine.

















































